
Omega Fatty Acids
What are omega fatty acids?
EPA - Omega 3
Eicosapentaenoic acid
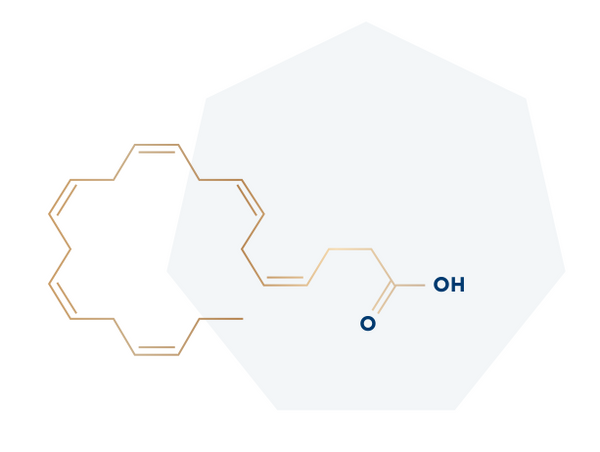

DHA - Omega 3
Docosahexaenoic acid

GLA - Omega 6
Gamma Linolenic acid
AA - Omega 6
Arachidonic Acid

Title






